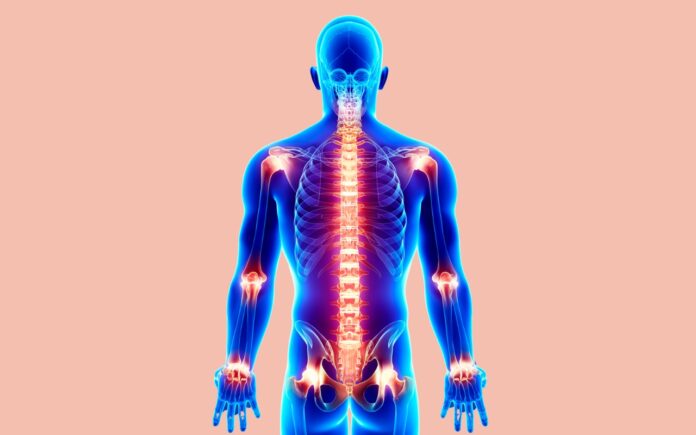
Inflammation, acute or chronic, is a typical response of the body's immune system to injuries or infections. While acute inflammation is essential for healing, chronic inflammation can lead to various health issues, including arthritis, diabetes, and heart disease. Fortunately, there are natural ways to manage and reduce inflammation, with exercise being one of the most effective methods. This article will explore the top exercises that can help reduce pain and inflammation naturally, offering a comprehensive guide for anyone looking to improve their health and quality of life.
Regular exercise provides numerous benefits, from enhancing cardiovascular health to boosting mental well-being. However, when it comes to reducing pain and inflammation, certain exercises are more beneficial than others. The key is finding a balance between physical activity and rest, ensuring the body remains active without exacerbating inflammation.
Understanding Inflammation and Its Causes
Before delving into specific exercises, it's essential to understand inflammation and its causes. Inflammation is the body's way of protecting itself from harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. The process involves the immune system releasing white blood cells and other chemicals to fight off invaders and promote healing.
While acute inflammation is a short-term response that typically resolves independently, chronic inflammation persists over time, often leading to prolonged pain and tissue damage. Common causes of chronic inflammation include:
- Low levels of physical activity: Sedentary lifestyles contribute to poor circulation and reduced immune function, exacerbating inflammation.
- Chronic stress: Persistent stress triggers the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, which can lead to ongoing inflammation.
- Poor diet: Consumption of processed foods, trans fats, and sugars can increase inflammation, while a diet rich in antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids can help reduce it.
- Obesity: Excess weight, particularly visceral fat, produces pro-inflammatory substances that can lead to chronic inflammation.
- Environmental toxins: Exposure to pollutants, chemicals, and smoking can contribute to inflammation.
Reducing inflammation through lifestyle changes, such as adopting a healthy diet and regular exercise, can significantly improve overall health.
The Role of Exercise in Reducing Inflammation
Exercise may initially seem counterintuitive when considering inflammation, as intense physical activity can potentially cause tissue damage and subsequent inflammation. However, moderate and regular exercise has been shown to have an anti-inflammatory effect on the body. Exercises like yoga, swimming, cycling, and resistance training can help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain.
Recent studies published in Brain, Behavior, and Immunity have found that even a 20-minute exercise session can boost the immune system, eliciting an anti-inflammatory response. This response is particularly beneficial for managing chronic conditions associated with inflammation, such as arthritis, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. By incorporating moderate exercise into daily routines, individuals can experience reduced inflammation and improved joint health.
Top Exercises to Combat Inflammation
Yoga
Yoga is renowned for its ability to reduce stress, which significantly contributes to inflammation. By focusing on breath control, slow movements, and stretching, yoga helps improve flexibility, strength, and balance. These benefits are particularly crucial for individuals suffering from joint pain, as they can enhance mobility and reduce stiffness.
Moreover, yoga's emphasis on mindfulness and relaxation can lower cortisol levels, a hormone associated with stress and inflammation. Practicing yoga regularly can improve both physical and mental well-being, making it an excellent choice for reducing pain and inflammation.
Walking
Walking is a simple yet highly effective way to combat inflammation. Regular walking helps maintain joint flexibility, improves cardiovascular health, and boosts mood. Although moving may seem counterproductive when experiencing joint pain, staying too sedentary can worsen stiffness and discomfort.
Incorporating short walks into daily routines, such as taking a 10-minute walk several times daily, can significantly alleviate joint pain and reduce inflammation. Walking outdoors also provides the added benefit of vitamin D from sunlight, further supporting immune function and hormonal balance.
Cycling
Cycling is another low-impact exercise that offers substantial benefits for reducing inflammation. This activity is particularly suitable for individuals with joint pain or those recovering from surgery, as it provides a cardiovascular workout without putting excessive strain on the joints.
Whether cycling outdoors or participating in a spin class, this exercise promotes joint mobility, enhances cardiovascular health, and releases endorphins, which are natural pain relievers. Regular cycling can lead to improved joint function and reduced inflammation over time.
Swimming
Swimming is often considered one of the best exercises for individuals with joint pain due to its low-impact nature. The buoyancy of water supports the body, reducing the strain on joints while providing resistance that helps build strength and flexibility.
Swimming also improves cardiovascular health and promotes a good range of motion, essential for preventing and managing inflammation. Regular swimming sessions can enhance overall fitness and reduce pain, making it a top choice for those looking to manage inflammation naturally.
Resistance Training
Resistance training, which includes exercises using weights, resistance bands, or body weight, is highly effective for reducing inflammation and strengthening muscles. This type of exercise is commonly used in physical therapy to improve strength, range of motion, and overall joint health.
By building muscle strength, resistance training supports the joints and reduces the likelihood of injuries. It also promotes cardiovascular health and releases endorphins, reducing pain and improving mood. Incorporating resistance training into a fitness routine can significantly reduce inflammation and long-term health benefits.
Lifestyle and Dietary Considerations
While exercise plays a crucial role in reducing inflammation, adopting a holistic approach that includes dietary and lifestyle changes is essential. A diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods can complement the benefits of exercise, further reducing inflammation and improving overall health.
Anti-Inflammatory Diet
Certain foods have been shown to reduce inflammation, while others can exacerbate it. To manage inflammation effectively, consider incorporating the following dietary changes:
- Increase intake of fruits and vegetables: Foods like berries, leafy greens, beets, and avocados are high in antioxidants, which help fight inflammation.
- Consume fermented foods: Yogurt, kefir, kimchi, and other fermented foods contain live microbes that can reduce inflammatory markers, such as interleukin 6 (IL-6).
- Focus on omega-3 fatty acids: Fatty fish like salmon, tuna, and mackerel, as well as walnuts and flaxseeds, are excellent sources of omega-3s, which help regulate inflammation.
- Reduce red meat consumption: Red meat can be pro-inflammatory, so try substituting it with fish, nuts, or plant-based proteins.
- Limit sugar and processed foods: High-sugar and processed foods can increase inflammation; opting for whole foods and minimally processed options is better.
For more information on anti-inflammatory diets, visit Mayo Clinic.
Lifestyle Changes
In addition to dietary modifications, specific lifestyle changes can further reduce inflammation:
- Manage stress: Chronic stress is a significant contributor to inflammation. Meditation, yoga, and mindfulness can help reduce stress levels.
- Get adequate sleep: Quality sleep is essential for overall health and reducing inflammation. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night.
- Avoid smoking and limit alcohol: Both smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can increase inflammation. Quitting smoking and moderating alcohol intake can lead to significant health improvements.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Obesity is closely linked to inflammation, so maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise is crucial.
For additional tips on managing inflammation through lifestyle changes, check out Cleveland Clinic.
Combining Exercise with Other Treatments
While exercise and lifestyle changes effectively manage inflammation, some individuals may require additional treatments, particularly if they suffer from severe or persistent inflammation. Working with a healthcare provider to develop a comprehensive treatment plan can ensure the best outcomes.
Medications
Several medications can help reduce inflammation, including nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, and immunosuppressants. These medications can effectively control symptoms, but they are often best used with lifestyle changes.
Supplements
Certain supplements, such as omega-3 fatty acids, zinc, and vitamins C and D, have anti-inflammatory properties. However, talking to a healthcare provider before starting any new supplements is essential to ensure they are safe and appropriate for individual needs.
For more information on medications and supplements for managing inflammation, visit WebMD.
Creating a Personalized Exercise Plan
When incorporating exercise into an anti-inflammatory routine, choosing enjoyable and sustainable activities is essential. A personalized exercise plan can help ensure consistency and maximize benefits.
Assessing Fitness Levels
Before starting a new exercise program, assessing current fitness levels and any existing health conditions is crucial. Consulting with a healthcare provider or physical therapist can help identify appropriate exercises and avoid activities that may exacerbate inflammation.
Setting Realistic Goals
Setting realistic and achievable goals is essential for maintaining motivation and tracking progress. Start with small, manageable goals, such as taking a short walk each day or attending a weekly yoga class, and gradually increase the intensity and duration of workouts.
Balancing Activity and Rest
Finding the right balance between activity and rest is crucial for managing inflammation. While regular exercise is beneficial, overtraining or pushing the body too hard can increase inflammation. Incorporating rest days and listening to the body can help prevent this.
Monitoring Progress
Monitoring progress can help identify what works best and make necessary adjustments to the exercise routine. Keeping a journal of workouts, noting any changes in pain or inflammation, and discussing progress with a healthcare provider can provide valuable insights.
Conclusion
Reducing pain and inflammation naturally through exercise is an achievable and effective strategy that can significantly improve overall health and well-being. By incorporating activities such as yoga, walking, cycling, swimming, and resistance training into daily routines, individuals can experience reduced inflammation, enhanced joint function, and improved quality of life. Coupled with a healthy diet and lifestyle changes, these exercises offer a comprehensive approach to managing and reducing chronic inflammation.
For more information on inflammation and ways to reduce it, visit the following resources:
- Elite Sports Medicine + Orthopedics
- Cleveland Clinic
- Mayo Clinic
- WebMD
By embracing these recommendations and making gradual changes, anyone can take control of their inflammatory response and enjoy the benefits of a healthier, more active lifestyle.













![Bowflex Max Total: 2024 Fitness Workout Exercise Machine [Review] Bowflex Max Total: 2020 Equipment Review For Complete Upper and Lower Body Workout](https://www.advancedliving.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/12/Bowflex-Max-Total-218x150.jpg)